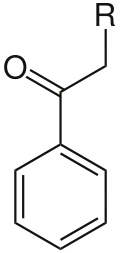
Structure of a compound containing a phenacyl group
In organic chemistry, a phenacyl group is an aromatic substituent that consists of a phenyl group attached to an acyl group. A molecule containing a phenacyl group has the formula RCH2(CO)C6H5 and the structure shown to the right. Here, R denotes the remainder of the molecule; for instance, if R is Br, then the compound could be called "phenacyl bromide". Note however that in the standard IUPAC nomenclature this compound would instead be called "2-bromo-1-phenylethanone".
Examples
- Phenacyl chloride is also known as CN gas.
- Phenacyl bromide, a toxic chemical mainly used in the production of other chemicals.
- N-phenacyl thiazolium bromide, a compound that breaks cross-links in Advanced glycation end products.
External links
 Media related to Phenacyl group at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Phenacyl group at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.