| Scottish Gaelic name | Siùna[1] |
|---|---|
| Meaning of name | Probably "sea island" from Norse[1] |
| Location | |
 Shuna Island Shuna shown within Argyll and Bute | |
| OS grid reference | NM916490 |
| Coordinates | 56°35′24″N 5°23′42″W / 56.59°N 5.395°W |
| Physical geography | |
| Island group | Loch Linnhe |
| Area | 155 ha (383 acres) |
| Area rank | 121 [2] |
| Highest elevation | Tom an t-Seallaidh 71 m (233 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Country | Scotland |
| Council area | Argyll and Bute |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 0[3] |
| References | [4][5] |

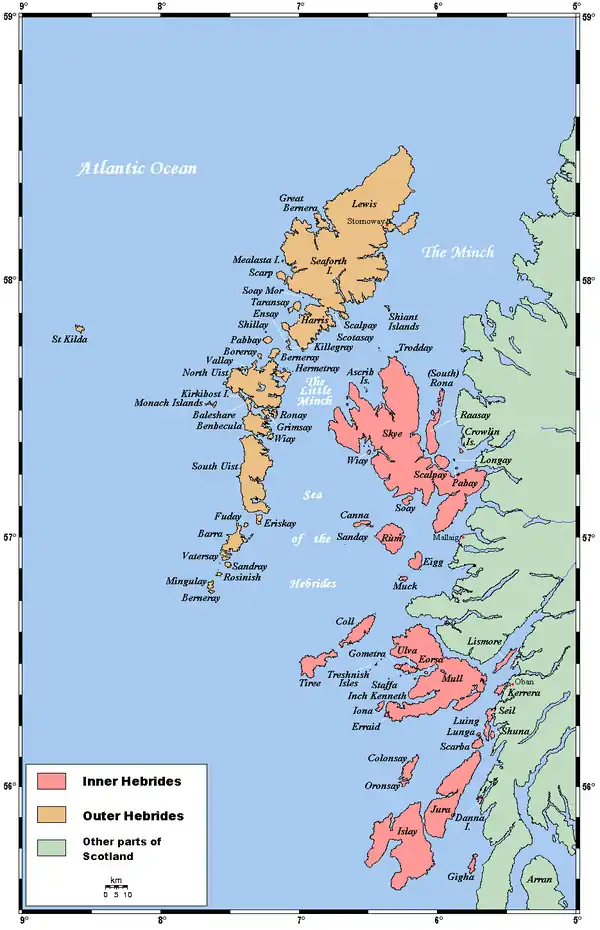
Shuna Island[6] or simply Shuna is an island in Loch Linnhe, offshore from Appin, in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The island is approximately two kilometres (1+1⁄4 miles) long and one kilometre (5⁄8 mi) wide, and extends to some 155 ha (383 acres) in total. The island is characterised by a table topped hill at its southern end.[7] The name Shuna is probably derived from the Norse, for "sea island".[1] The island is separated from Appin by the Sound of Shuna.
Shuna is recorded in a late 16th-century document as belonging to John Stewart, the Laird of Appin.[5] He may have built Castle Shuna, a small tower-house, which is now in ruins and lies at the south end.[8] In the 18th century, Shuna Farmhouse replaced Castle Shuna as the residence on the island: it is a Category B listed traditional farmhouse dating from the 1740s.[9] Opposite Castle Shuna, at the head of Loch Laich, is the island fortress of Castle Stalker, also historically a possession of the Stewarts of Appin.[10]
The island forms part of the Lynn of Lorn National Scenic Area, one of 40 in Scotland.[11]
In 2012 the island was placed on sale via agents Savills for £1.85 million.[12]
Notes and references
- 1 2 3 Mac an Tàilleir p. 105
- ↑ Area and population ranks: there are c. 300 islands over 20 ha in extent and 93 permanently inhabited islands were listed in the 2011 census.
- ↑ General Register Office for Scotland (28 November 2003) Scotland's Census 2001 – Occasional Paper No 10: Statistics for Inhabited Islands. Retrieved 26 February 2012.
- ↑ Ordnance Survey. OS Maps Online (Map). 1:25,000. Leisure.
- 1 2 Haswell-Smith (2004) pp. 117-18
- ↑ "Shuna Island". Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 15 February 2020.
- ↑ "Overview of Shuna". Gazetteer for Scotland. Retrieved 12 December 2007.
- ↑ "Castle Shuna". Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland. Retrieved 12 December 2007.
- ↑ Historic Environment Scotland. "Shuna Farmhouse (Category B Listed Building) (LB12343)". Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- ↑ Historic Environment Scotland. "Castle Stalker (Category A Listed Building) (LB12345)". Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- ↑ "National Scenic Areas" Archived 2017-03-11 at the Wayback Machine. SNH. Retrieved 30 Mar 2011.
- ↑ Welsh, Susan (5 June 2012) "Buy a piece of paradise". Glasgow. The Herald.
Further reading
- Haswell-Smith, Hamish (2004). The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh: Canongate. ISBN 978-1-84195-454-7.
- Mac an Tàilleir, Iain (2003) Ainmean-àite/Placenames. (pdf) Pàrlamaid na h-Alba. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
56°35′14″N 5°23′43″W / 56.58722°N 5.39528°W