Artemotil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
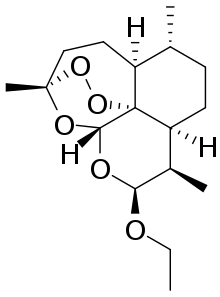
| Formula | C17H28O5 |
| Molar mass | 312.406 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Artemotil (INN; also known as β-arteether[1]), is a fast acting blood schizonticide specifically indicated for the treatment of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria and cerebral malaria cases.[2] It is a semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin, a natural product of the Chinese plant Artemisia annua. It is currently only used as a second line drug in severe cases of malaria.
References
- ↑ "The International Pharmacopoeia - Sixth Edition - Artemotil" (PDF). 2016. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ↑ Yeates RA (April 2002). "Artemotil Artecef". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 3 (4). London, England: 545–9. PMID 12090721.
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.