Enoximone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Perfan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 85% |
| Metabolism | Liver (oxidation) |
| Elimination half-life | 4 to 10 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (60 to 70%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
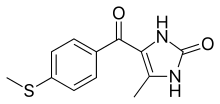
| Formula | C12H12N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 248.30 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 255 to 258 °C (491 to 496 °F) (decomposes) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Enoximone (INN, trade name Perfan) is an imidazole phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and is selective for phosphodiesterase 3.[1]
References
- ↑ Boldt J, Suttner S (September 2007). "Combined use of ultra-short acting beta-blocker esmolol and intravenous phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor enoximone". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 8 (13): 2135–47. doi:10.1517/14656566.8.13.2135. PMID 17714066. S2CID 46021219.
External links
 Media related to Enoximone at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Enoximone at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.