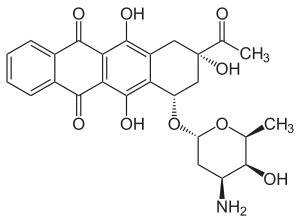
Idarubicin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌaɪdəˈruːbɪsɪn/ |
| Trade names | Zavedos, Idamycin, others |
| Other names | Idarubicin hydrochloride, 4-demethoxydaunorubicin, 9-acetyl-7-(4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydropyran-2-yl)oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Anthracycline[1] |
| Main uses | Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), breast cancer[2][3] |
| Side effects | Nausea, hair loss, abdominal pain, diarrhea, bleeding, mouth inflammation, fever, headache[2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a691004 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 97% |
| Elimination half-life | 22 hours |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H27NO9 |
| Molar mass | 497.500 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Idarubicin, sold under the brand name Zavedos and Idamycin, is a medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and breast cancer.[2][3] It is often used with cytarabine.[2] It is given by injection into a vein or taken by mouth.[2][3]
Common side effects include nausea, hair loss, abdominal pain, diarrhea, bleeding, mouth inflammation, fever, and headache.[2] Other side effects may include heart failure, arrhythmias, bone marrow suppression, high uric acid, liver problems, kidney problems.[2] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[2] It is an anthracycline and acts similar to daunorubicin.[1]
Idarubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1990.[2] In the United Kingdom 10 mg for injection costs the NHS about £175 as of 2021.[3] In the United States this amount costs about 70 USD.[4]
Medical use
Dosage
The typical dose is 12 to 45 mg/m2 body surface area though different doses may be used in those with liver or kidney problems.[1][3]
Side effects
Diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting are common among patients treated with idarubicin.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 "Doxorubicin". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. Archived from the original on 16 May 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "IDArubicin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 948. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Idarubicin Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ↑ "Idarubicin Side Effects: Common, Severe, Long Term". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2019-06-21. Retrieved 2019-06-21.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- Idarubicin bound to proteins Archived 2021-10-31 at the Wayback Machine in the PDB