List of nail conditions
This is a list of terms used to describe nails in nail diseases.[1][2] Some are normal variants.[3] Most can be diagnosed by their appearance.[4] There may be a change in color, shape, surface, or attachment of the nail.[5][6][7]
Types
Nail conditions
A-F
| Name | Types | Signs and symptoms | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anonychia[9] | The absence of finger- and/or toenails.[9] | .jpg.webp) |
||
| Beau’s lines | Varying depths of transverse grooves across the nail due to reduced growth or arrest of nail growth.[10] | .jpg.webp) |
||
| Chevron nail | Also known as Herringbone nail, is a transient fingernail ridge pattern seen in children.[1] | |||
| Chromonychia | Brown-black nails (melanonychia)[11] | .jpg.webp) |
Acquired abnormalities of nail color[8] | |
| Blue nails[9] | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Green nails | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Red nails[11] | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| White nails: Terry's nails[9] | ||||
| Clubbing[10] | Congenital | |||
| Acquired | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Congenital onychodysplasia of the index fingers | ||||
| Darier disease | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Drug side effect | .jpg.webp) | |||
G-I
| Name | Description | Image | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Habit-tic deformity[11] | 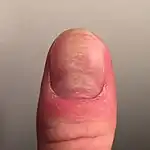 | ||
| Half and half nail[9] | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Hangnail | An annoying torn piece of skin, next to a fingernail or toenail.[1] | 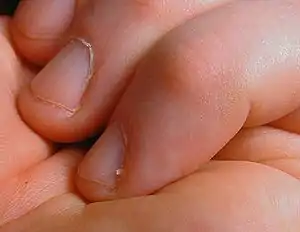 | |
| Hapalonychia | 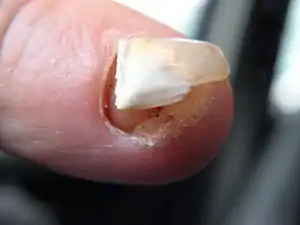 | ||
| Hook nail | 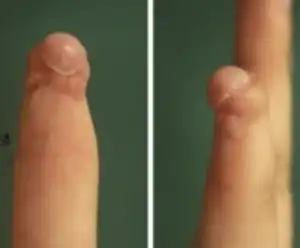 | ||
| Hutchinson sign[12] | |||
| Ingrown nail | Ingrowing toenail[10] | 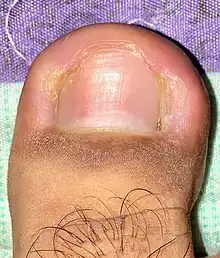 |
|
| Infected ingrowing toenail | 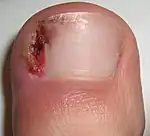 |
||
J-N
| Name | Description | Image | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Koilonychia[3] |
| .jpg.webp) | |
| Lichen planus of nails | 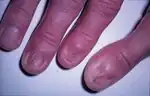 | ||
| Mees' lines[9] | 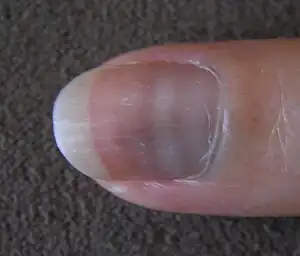 | ||
| Muehrcke's nails[9] | 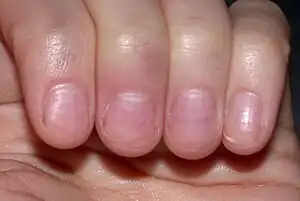 | ||
| Myxoid cyst | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Nail–patella syndrome | 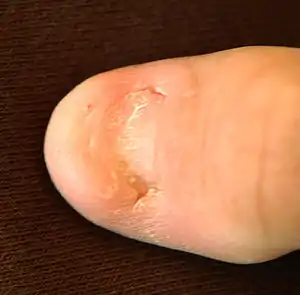 | ||
| Nail splitting | .jpg.webp) | ||
O
| Name | Description | Image | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onychauxis[9] | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Onychia | 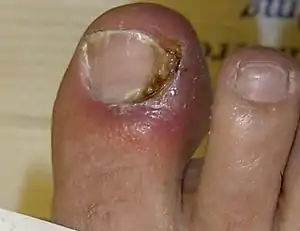 | ||
| Onychogryphosis[9] | .jpg.webp) | Acquired deformities of the nail plate[8] | |
| Onycholysis[6] | Psoriatic | .jpg.webp) |
Acquired deformities of the nail plate[8] |
| Drug-induced
(Tetrayclines, taxanes)[6] |
.jpg.webp) |
Acquired deformities of the nail plate[8] | |
| Infections
(Candida, dermatophytes, HPV)[6] |
.jpg.webp) |
||
| Endocrine
(Hyperthyroidism)[6] |
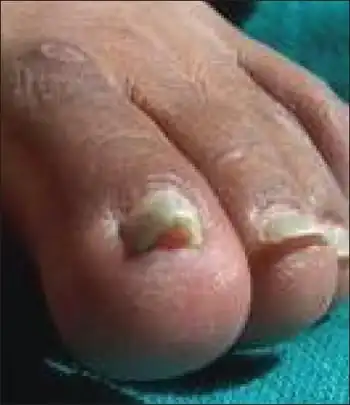 |
||
| Tumor
(Subungal exostosis, SCC)[6] |
|||
| Trauma[6] | |||
| Onychophosis | |||
| Onychomadesis[3] | Shedding of nails from base[3]
New nail simultaneously appearing[3] Following viral infection[3] |
.jpg.webp) | |
| Onychomatricoma | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Onychomycosis | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Onychorrhexis[9] | Excessive ridges from frequent hand washing.[9] | .jpg.webp) | |
| Onychoschizia[9] | |||
P
| Name | Types | Signs and symptomsImage | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paronychia[14] | Acute[14] | 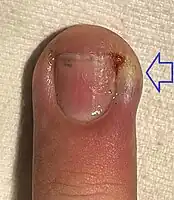 |
||
| Chronic[14] | 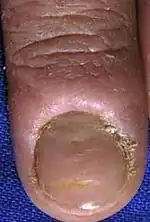 |
|||
| Bacterial[14] | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Viral[14] | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Fungal[14] | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Non-infectious[14] | .jpg.webp) |
|||
| Pachyonychia congenita | .jpg.webp)
| Acquired deformities of the nail plate[8] | ||
| Periungal fibroma | ||||
| Pincer nail | .jpg.webp) | |||
| Pitted nails[9] | Small, pinpoint depressions in a nail, which may give a clue to diagnosing conditions such as psoriasis and alopecia areata.[1][9] | .jpg.webp) | Acquired deformities of the nail plate[8] | |
| Platonychia | ||||
| Plummer's nail |  | |||
| Psoriatic onychodystrophy | .jpg.webp) | |||
| Pterygium inversus unguis[1] | 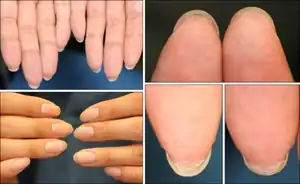
| |||
| Pterygium unguis[1] | 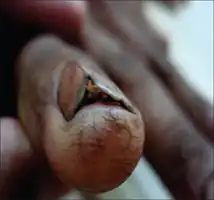 | |||
Q-Z
| Name | Description | Image | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Racquet nail | 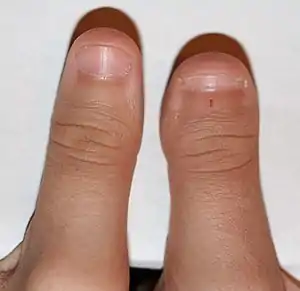 | ||
| Shell nail syndrome | |||
| Splinter hemorrhage[9] | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Subungal exostosis | |||
| Subungual hematoma |  | Certain disorders affecting the nails or perionychium[8] | |
| Trachonychia[9] | .jpg.webp) | ||
| Yellow nail syndrome[9] | [10] | 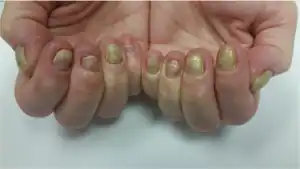 | Acquired abnormalities of nail color[8] |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "33. Diseases of the skin appendages". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 750–793. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2023-04-12. Retrieved 2023-04-12.
- ↑ "Nail terminology | DermNet NZ". dermnetnz.org. Archived from the original on 12 April 2022. Retrieved 15 April 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Bellet, Jane Sanders (2021). "Paediatric nail disorders". In Lipner, Shari (ed.). Nail Disorders: Diagnosis and Management, An Issue of Dermatologic Clinics. Philadelphia: Elsevier. pp. 231–244. ISBN 978-0-323-70923-1. Archived from the original on 2023-07-01. Retrieved 2023-04-12.
- ↑ Singal, Archana; Neema, Shekhar; Kumar, Piyush, eds. (2019). Nail Disorders: A Comprehensive Approach. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-8153-7834-1. Archived from the original on 2023-07-01. Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ↑ Berker, David de (2019). "20. Diseases of the nails". In Morris-Jones, Rachael (ed.). ABC of Dermatology (7th ed.). Hoboken: Wiley Blackwell. pp. 165–174. ISBN 978-1-119-48899-6. Archived from the original on 2023-07-01. Retrieved 2023-06-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Bolognia, Jean L.; Schaffer, Julie V.; Duncan, Karynne O.; Ko, Christine (2021). "58. Nail disorders". Dermatology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 561–573. ISBN 978-0-323-62453-4. Archived from the original on 2024-01-20. Retrieved 2024-01-17.
- ↑ Saavedra, Arturo; Roh, Ellen K.; Mikailov, Anar (2023). "32.Disorders of the nail apparatus". Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology, 9/e (9th ed.). New York: McGraw Hill Professional. pp. 849–872. ISBN 978-1-264-27801-5. Archived from the original on 2023-12-31. Retrieved 2024-01-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics". icd.who.int. Archived from the original on 1 August 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Johnstone, Ronald B. (2017). "2. Diagnostic clues and "need-to-know" items". Weedon's Skin Pathology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 30–33. ISBN 978-0-7020-6830-0. Archived from the original on 2023-07-01. Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- 1 2 3 4 Tosti, Antonella (2020). "413. Diseases of hair and nails". In Goldman, Lee; Schafer, Andrew I. (eds.). Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Vol. 2 (26th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier. pp. 2660–2661. ISBN 978-0-323-53266-2. Archived from the original on 2023-06-30. Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- 1 2 3 Sloan, Brett; Muzumdar, Sonal (2022). "15. Conditions that frequently affect a single nail". In Waldman, Reid A.; Grant-Kels, Jane M. (eds.). Dermatology for the Primary Care Provider. Philadelphia: Elsevier. pp. 268–272. ISBN 978-0-323-71236-1. Archived from the original on 2023-07-30. Retrieved 2023-07-28.
- ↑ Bose, Shiti; Khandare, Manish; Kulkarni, Dipak; Joseph, Jebin (January 2023). "A Compendium of Common Signs in Dermoscopy, Trichoscopy, and Onychoscopy". Clinical Dermatology Review. 7 (1): 44. doi:10.4103/cdr.cdr_74_21. ISSN 2542-551X. Archived from the original on 2023-03-25. Retrieved 2023-07-28.
- ↑ Berker, David de (2019). "20. Diseases of the nails". In Morris-Jones, Rachael (ed.). ABC of Dermatology (7th ed.). Hoboken: Wiley Blackwell. p. 168. ISBN 978-1-119-48899-6. Archived from the original on 2023-07-01. Retrieved 2023-06-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Dulski, Anne; Edwards, Christopher W. (2022). "Paronychia". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 2022-08-15. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.