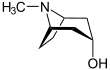
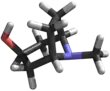
Tropine
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,3r,5S)-8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol | |||
| Other names
α-Tropine; Tropanol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.986 | ||
| MeSH | Tropine | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C8H15NO | ||
| Molar mass | 141.214 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White hygroscopic crystalline powder[1][2][3] or plates | ||
| Odor | Amine-like[2] | ||
| Density | 1.045 g/cm3 at 25 °C[2] 1.016 g/cm3 at 100 °C | ||
| Melting point | 64 °C (147 °F; 337 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 233 °C (451 °F; 506 K) | ||
| Solubility | Very soluble in water, diethyl ether, ethanol[4] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards |
Toxic | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
Pictograms |
  | ||
Signal word |
Danger | ||
Hazard statements |
H301, H302, H312, H332 | ||
Precautionary statements |
P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P316, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P317, P321, P330, P362+P364, P405, P501 | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Tropine is a derivative of tropane containing a hydroxyl group at the third carbon. It is also called 3-tropanol.[4] It is a poisonous white hygroscopic crystalline powder.[3] It is a heterocyclic alcohol and an amine.[3]
Tropine is a central building block of many chemicals active in the nervous system, including tropane alkaloids. Some of these compounds, such as long-acting muscarinic antagonists are used as medicines because of these effects.[5]
Occurrence
Tropine is a natural product found in the plants of deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) and devil's trumpet (Datura stramonium).[1]
Chemistry
Synthesis
It can be prepared by hydrolysis of atropine[6] or other solanaceous alkaloids.[3]
See also
- Pseudotropine
- Atropine
- Tropinone
- Tropane alkaloid
References
- 1 2 3 "8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol".
- 1 2 3 4 https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/GB/en/sds/aldrich/93550
- 1 2 3 4 "Medical Definition of TROPINE".
- 1 2 Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–564, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Ping, Yu; Li, Xiaodong; You, Wenjing; Li, Guoqiang; Yang, Mengquan; Wei, Wenping; Zhou, Zhihua; Xiao, Youli (10 June 2019). "Production of the Plant-Derived Tropine and Pseudotropine in Yeast". ACS Synthetic Biology. 8 (6): 1257–1262. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.9b00152. PMID 31181154. S2CID 184484993.
- ↑ "Cocaine analog in two steps from native plant material".
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.