 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
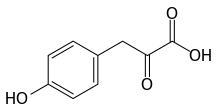
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxopropanoic acid | |
| Other names
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.322 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 180.157 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (4-HPPA) is an intermediate in the metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. The aromatic side chain of phenylalanine is hydroxylated by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase to form tyrosine. The conversion from tyrosine to 4-HPPA is in turn catalyzed by tyrosine aminotransferase.[1] Additionally, 4-HPPA can be converted to homogentisic acid which is one of the precursors to ochronotic pigment.[2]
It is an intermediary compound in the biosynthesis of scytonemin.
See also
References
- ↑ Brand, Larry; Harper, Alfred (1974). "Effect of glucagon on phenylalanine metabolism and phenylalanine-degrading enzymes in the rat". Biochemical Journal. 142 (2): 231–45. doi:10.1042/bj1420231. PMC 1168273. PMID 4155291.
- ↑ Denoya, Claudio; Skinner, Deborah; Morgenstern, Margaret (September 1994). "A Streptomyces avermitilis gene encoding a 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid dioxygenase-like protein that directs the production of homogentisic acid and an ochronotic pigment in Escherichia coli". Journal of Bacteriology. 1 (17): 5312–5319. doi:10.1128/jb.176.17.5312-5319.1994. PMC 196716. PMID 8071207.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.