 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Aminoacetaldehyde | |
| Other names
H-Gly-al; glycynal | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H5NO | |
| Molar mass | 59.068 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
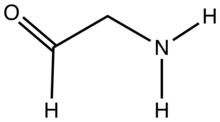
Aminoacetaldehyde is the organic compound with the formula OHCCH2NH2. Under the usual laboratory conditions, it is unstable, tending instead to undergo self-condensation.[1] Aminoacetaldehyde diethylacetal is a stable surrogate.[2]
In nature, aminoacetaldehyde is produced by oxygenation of taurine catalyzed by taurine dioxygenase, which produces the sulfite H2NCH2CH(OH)SO3−.
See also
References
- ↑ Fisher, Lawrence E.; Muchowski, Joseph M. (1990). "Synthesis of α-Aminoaldehydes and α-Aminoketone. A Review". Organic Preparations and Procedures International. 22 (4): 399–484. doi:10.1080/00304949009356309.
- ↑ Amato, Francesco; Marcaccini, Stefano (2005). "2,2-Diethoxy-1-Isocyanoethane". Organic Syntheses. 82: 18. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.082.0018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.