| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.708 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H28N4O |
| Molar mass | 316.449 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Butalamine is a vasodilator.[1]
Synthesis
Check with imolamine (alternate nitrogen reacts)
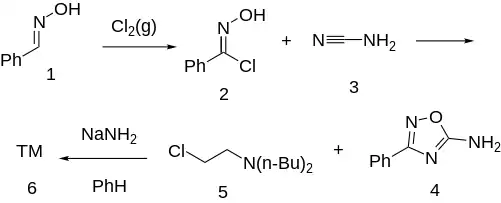
USA Ex 9: The halogenation of benzamidoxime [932-90-1] [622-31-1] (1) with chlorine and subsequent reaction with cyanamide (3) gives 5-amino-3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole [3663-37-4] (4). Base catalyzed alkylation with dibutylaminoethyl chloride [13422-90-7] (5) completes the synthesis of butalamine (6).
References
- ↑ Sterne J (April 1976). "[Butalamine hydrochloride. A new vasoactive substance]". Fortschritte Der Medizin (in German). 94 (11): 657–9. PMID 823083.
- ↑ Aron-samuel Jan Marcel Didier, FR3334M (1965 to Jan Marcel).
- ↑ Japan. Pat., 76 108 068, (1976); CA, 87, 5981b
- ↑ Aron-Samuel Jan Marcel Didier, Sterne Jean Jacques, U.S. Patent 3,338,899 (1967 to).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.