 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
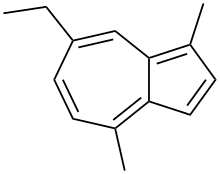
| Preferred IUPAC name
7-Ethyl-1,4-dimethylazulene | |
| Other names
1,4-Dimethyl-7-ethylazulene; Ba 2784; Camazulene; Chamazulen; Dimethulen; Dimethulene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.682 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16 | |
| Molar mass | 184.282 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Blue oil[1] |
| Density | 0.9883 (at 20 °C)[1] |
| Boiling point | 161 °C (322 °F; 434 K) (at 12 mmHg)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
3 g/kg (i.m., mouse)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
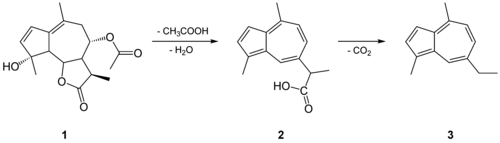
Chamazulene is an aromatic chemical compound with the molecular formula C14H16 found in a variety of plants including in chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla), wormwood (Artemisia absinthium), and yarrow (Achillea millefolium).[1] It is a blue-violet derivative of azulene which is biosynthesized from the sesquiterpene matricin.[2]
Chamazulene has anti-inflammatory properties in vivo and inhibits the CYP1A2 enzyme.[2]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.