 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
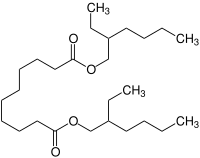
| IUPAC name
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) decanedioate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[Heptane-3-yl-(-3-methane-1,1-diyl)-] decanedioate | |
| Other names
Di(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate, Proviplast 1988, dioctyl sebacate (archaic)[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.145 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H50O4 | |
| Molar mass | 426.682 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.9 of water |
| Melting point | −48 °C (−54 °F; 225 K) |
| Boiling point | 256 °C (493 °F; 529 K) at 0.7 kPa |
| none | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.000024 Pa at 37 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
reacts with oxidants |
| Flash point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) open cup |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
5 g/kg (rat, orally)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dioctyl sebacate (also di(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate, commonly abbreviated as DOS, DEHS, and BEHS) is an organic compound which is the diester of sebacic acid and 2-ethylhexanol. It is an oily colorless liquid and is used as a plasticizer, including in the explosive C4.[3] It has also found use in Dot 5 brake fluid, in ester-based engine oils and additives, as seed particle for Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) and as a model compound that forms stable aerosols.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.