 | |
| Mission type | Optical reconnaissance |
|---|---|
| Operator | US Air Force/NRO |
| Mission duration | Failed to orbit |
| Spacecraft properties | |
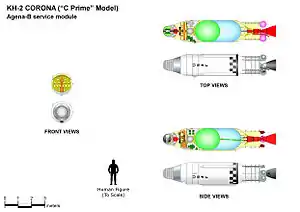
| Spacecraft type | Corona KH-2 |
| Bus | Agena-B |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed |
| Launch mass | 1,150 kilograms (2,540 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 30 March 1961, 20:34:43 UTC |
| Rocket | Thor DM-21 Agena-B 300 |
| Launch site | Vandenberg LC-1 launch pad 75-3-4 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Epoch | Planned |
.gif)
Discoverer 22, also known as Corona 9015, was an American optical reconnaissance satellite which was lost in a launch failure in 1961. It was the fourth of ten Corona KH-2 satellites, based on the Agena-B.[1]
The launch of Discoverer 22 occurred at 20:34:43 UTC on 30 March 1961. A Thor DM-21 Agena-B rocket was used, flying from launch pad 75-3-4 at the Vandenberg Air Force Base.[2] Due to a malfunction of the rocket's second stage, it failed to achieve orbit.[3]
Discoverer 22 was to have operated in a low Earth orbit. It had a mass of 1,150 kilograms (2,540 lb),[4] and was equipped with a panoramic camera with a focal length of 61 centimetres (24 in), which had a maximum resolution of 7.6 metres (25 ft).[5] Images were to have been recorded onto 70-millimeter (2.8 in) film, and returned in a Satellite Recovery Vehicle. The Satellite Recovery Vehicle carried aboard Discoverer 22 was SRV-509.[4]
References
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter. "KH-2 Corona". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 23 October 2020.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ↑ Pike, John (9 September 2000). "KH-2 Corona". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- 1 2 Wade, Mark. "KH-2". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 23 October 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ↑ "Corona". Mission and Spacecraft Library. NASA. Archived from the original on 3 October 2007. Retrieved 23 June 2010.