 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
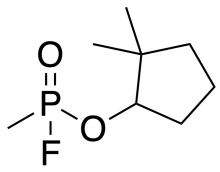
| IUPAC name
2-[fluoro(methyl)phosphoryl]oxy-1,1-dimethylcyclopentane | |
| Other names
2,2-Dimethylcyclopentyl methylphosphonofluoridate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16FO2P | |
| Molar mass | 194.186 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
GP is an organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series,[1] with a relatively slow rate of hydrolysis, and thus high stability and persistence in the environment.[2]
References
- ↑ Ellison DH (2008). Handbook of Chemical and Biological Warfare Agents (Second ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-849-31434-6.
- ↑ Harvey SP, McMahon LR, Berg FJ (January 2020). "Hydrolysis and enzymatic degradation of Novichok nerve agents". Heliyon. 6 (1): e03153. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03153. PMC 7002793. PMID 32042950.
| Animal toxins | |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | |
| Cyanotoxins | |
| Plant toxins | |
| Mycotoxins | |
| Pesticides | |
| Nerve agents | |
| Bicyclic phosphates | |
| Cholinergic neurotoxins |
|
| Other | |
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||
| Release (modulators) |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.