 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Imeron, Iomeron |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | none |
| Elimination half-life | 109±20 min |
| Excretion | via kidneys |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
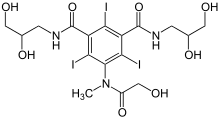
| Formula | C17H22I3N3O8 |
| Molar mass | 777.089 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Iomeprol is a pharmaceutical drug used as a radiocontrast agent in X-ray imaging. It is sold under the trade names Imeron and Iomeron.[1][2]
It is classified as a water-soluble, nephrotrophic, low osmolar X-ray contrast medium.[1] Low osmolar non-ionic agents are better tolerated and less likely to cause side effects than the high osmolar ionic agents.[1]
The substance is not metabolized in the human body but excreted in unchanged form. It is decomposed slowly and can therefore accumulate in the environment.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Rossiter D (2014). South African medicines formulary (11th ed.). Rondebosch, South Africa: Health and Medical Pub. Group of the South African Medical Association. ISBN 978-1-875098-30-9. OCLC 869772940.
- ↑ Haberfeld H, ed. (2020). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. Iomeron 300 mg J/ml-Infusionsflasche.
- ↑ Pfundstein P, Martin C, Schulz W, Seitz W, Ruth KM, Wille A, Steinbach A, Flottmann D (January 2015). "IC-ICP/MS-Analytik". GIT Labor-Fachzeitschrift (in German): 29–31.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.