 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl perchlorate | |
| Other names
Perchloric acid, methyl ester; | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3ClO4 | |
| Molar mass | 114.48 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | liquid |
| Boiling point | 52.0 °C (125.6 °F; 325.1 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | −14.8 ± 18.7 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
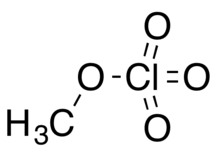
Methyl perchlorate is an organic chemical compound with the chemical formula CH3ClO4. Its molecular structure is a methyl group covalently bonded by a single bond to a perchlorate group, CH3−O−Cl(=O)3, in which chlorine has an oxidation state of +7. Like many other perchlorates, it is a high energy material. It is also a toxic alkylating agent and exposure to the vapor can cause death.[2] It can be prepared by treating iodomethane with a solution of silver perchlorate in benzene.
References
- ↑ Urben, Peter (2017). Bretherick's Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards. Elsevier. p. 116. ISBN 9780081010594.
- ↑ "Alkyl Perchlorate Esters - energeticchemical". Energeticchemical. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.