 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Methyl-1,3-thiazolidine-2-thione | |
| Other names
MTT, MTT 80, N-Methyl-2-thiazolidinethione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.014 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7NS2 | |
| Molar mass | 133.23 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 68–69 °C (154–156 °F; 341–342 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
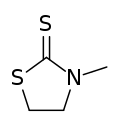
N-Methyl-2-thiazolidinethione is the organosulfur compound with the formula C2H4S(NCH3)CS. It is classified as a heterocycle called a thiazolidine. It is a colorless or off-white solid. It has gained attention as a proposed low toxicity replacement for ethylenethioureas, which are used as accelerators for the vulcanization of chloroprene rubbers.[1] The compound is prepared by reaction of N-methylethanolamine and carbon disulfide.
See also
- Mercaptobenzothiazole - a structurally similar, but aromatic, vulcanization accelerator
References
- ↑ Rüdiger Schubart (2000). "Dithiocarbamic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_001.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.