 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
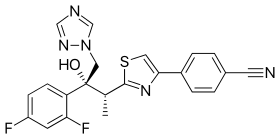
| Formula | C22H17F2N5OS |
| Molar mass | 437.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ravuconazole (codenamed BMS-207147 and ER-30346) is a potent triazole antifungal, the development of which was discontinued in 2007.[1] The drug has shown to have a similar spectrum of activity to voriconazole, with an increased half-life.[2] However, ravuconazole has limited activity against species of Fusarium, Scedosporium, and Zygomycetes.[3][4]
See also
- Albaconazole
- Fosravuconazole, a prodrug of ravuconazole
- Isavuconazole
References
- ↑ "Ravuconazole". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. Retrieved 12 November 2017.
- ↑ Pasqualotto AC, Denning DW. "Ravuconazole". The Aspergillus Website. Retrieved 18 February 2010.
- ↑ Pasqualotto AC, Thiele KO, Goldani LZ (February 2010). "Novel triazole antifungal drugs: focus on isavuconazole, ravuconazole and albaconazole". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 11 (2): 165–174. PMID 20112166.
- ↑ Pfaller MA, Messer SA, Hollis RJ, Jones RN (April 2002). "Antifungal activities of posaconazole, ravuconazole, and voriconazole compared to those of itraconazole and amphotericin B against 239 clinical isolates of Aspergillus spp. and other filamentous fungi: report from SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, 2000". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 46 (4): 1032–1037. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.4.1032-1037.2002. PMC 127116. PMID 11897586.
External links
 Media related to Ravuconazole at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ravuconazole at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.