| History of Cyprus |
|---|
 |
|
|
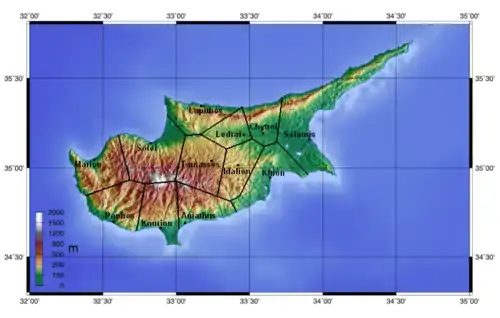
The ten city-kingdoms of ancient Cyprus were the Greek, Graeco-Phoenician or Graeco-Eteocypriot, states listed in an inscription of the Assyrian king Esarhaddon in 673-672 BC:[1]
- Paphos, Πάφος (Greek)
- Salamis, Σαλαμίς (Greek)
- Soloi, Σόλοι (Greek)
- Kourion, Κούριον (Greek)
- Chytroi, Χῦτροι (Greek)
- Kition, Κίτιον (Graeco-Phoenician)
- Amathus, Ἀμαθούς (Graeco-Amathusean)
- Idalion, Ἰδάλιον (Greek)
- Ledrai, Λῆδραι (Greek)
- Tamassos, Ταμασσός (Greek)
And later :
- Kyrenia, Κυρηνεία (Greek)
- Lapethos, Λάπηθος (Greek, Graeco-Phoenician for a short while)
- Marion, Μάριον (Greek)
References
- ↑ Sir Ernest Alfred Wallis Budge 1880, “The history of Esarhaddon (son of Sennacherib) king of Assyria” (The Names of the Twenty-two Kings, p. 104-108)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.