 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
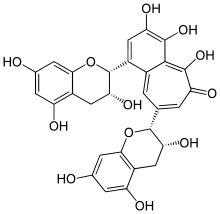
| Systematic IUPAC name
3,4,5-Trihydroxy-1,8-bis[(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-2-yl]-6H-benzo[7]annulen-6-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H24O12 | |
| Molar mass | 564.499 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Theaflavin (TF) and its derivatives, known collectively as theaflavins, are antioxidant polyphenols that are formed from the condensation of flavan-3-ols in tea leaves during the enzymatic oxidation (sometimes erroneously referred to as fermentation) of black tea. Theaflavin-3-gallate, theaflavin-3'-gallate, and theaflavin-3-3'-digallate are the main theaflavins.[1] Theaflavins are types of thearubigins, and are therefore reddish in color.
See also
References
- ↑ "Theaflavin Effectiveness, Safety, and Drug Interactions on RxList". rxlist.com. Archived from the original on 4 September 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.