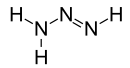| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Triazene | |||
| Other names
Azoimidamide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| 49028 | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H3N3 | |||
| Molar mass | 45.045 g·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions |
Triphosphane | ||
Related Binary azanes |
ammonia diazane triazane | ||
Related compounds |
Diazene Tetrazene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Triazene is an unsaturated inorganic compound having the chemical formula N3H3. It has one double bond and is the second-simplest member of the azene class of hydronitrogen compounds, after diimide. Triazenes are a class of organic compounds containing the functional group -N(H)-N=N-. Triazene, possibly along with its isomer triimide (HNNHNH), has been synthesized in electron-irradiated ices of ammonia and ammonia/dinitrogen and detected in the gas phase after sublimation.[1]
References
- ↑ Forstel, Tsegaw, Maksyutenko, Mebel, Sander, & Kaiser. "On the formation of N3H3 isomers in irradiated ammonia bearing ices: Triazene (H2NNNH) or Triimide (HNHNNH)", ChemPhysChem, 2016, 17, 2726.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.