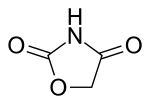
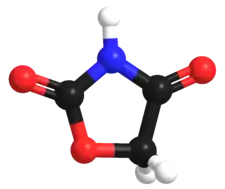
2,4-Oxazolidinedione
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Oxazolidine-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
2,4-Oxazolidenedione | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C3H3NO3 |
| Molar mass | 101.061 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 89–90 °C (192–194 °F; 362–363 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,4-Oxazolidinedione is an organic compound with the formula HN(CO)2OCH2. It is a white solid. The parent ring is not particularly important, but this core structure is found in a variety anticonvulsant drugs. The parent compound is obtained by treating chloroacetamide with bicarbonate.[1]
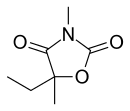
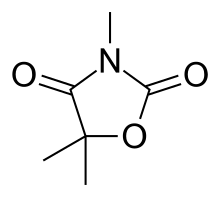
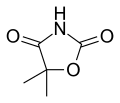 Dimethadione
Dimethadione
See also
- Glycine N-carboxyanhydride, the parent 2,5-oxazolidinedione
References
- ↑ Cesa, Stefania; Mucciante, Vittoria; Rossi, Leucio (1999). "Tetraethylammonium hydrogen carbonate in organic synthesis: Synthesis of oxazolidine-2,4-diones". Tetrahedron. 55: 193–200. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(98)01025-4.
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.