Valproate pivoxil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.071.502 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
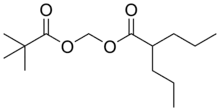
| Formula | C14H26O4 |
| Molar mass | 258.358 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Valproate pivoxil (Pivadin, Valproxen) is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy.[1] It is the pivaloyloxymethyl ester derivative of valproic acid.[2] It is likely a prodrug of valproic acid, as pivoxil esters are commonly employed to make prodrugs in medicinal chemistry.
See also
References
- ↑ Triggle DJ (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents. London: Chapman & Hall. ISBN 0-412-46630-9.
- ↑ Hall JA, Morton IK (1999). Concise dictionary of pharmacological agents: properties and synonyms. Kluwer Academic. p. 342. ISBN 0-7514-0499-3.
| Anticonvulsants | |
|---|---|
| Atypical antipsychotics | |
| Others |
|
| Transporter |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme |
| ||||
| Other |
| ||||
| |||||
| |
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators |
| Calcium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chloride |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Transient receptor potential channel modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.