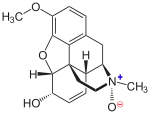
Codeine-N-oxide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1S,4S,5R,13R,14S,17R)-10-Methoxy-4-methyl-12-oxa-4-azapentacyclo[9.6.1.01,13.05,17.07,18]octadeca-7(18),8,10,15-tetraen-14-ol 4-oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.899 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C18H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 315.369 g·mol−1 |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Codeine-N-oxide (genocodeine) is an active metabolite of codeine.[2] It is an opiate listed as a Schedule I controlled substance.[3] It has a DEA ACSCN of 9053 and its annual manufacturing quota for 2013 was 602 grams.
Like morphine-N-oxide, it was studied as a potential pharmaceutical drug and is considerably weaker than codeine. The amine oxides of this type form as oxidation products of the parent chemical; virtually every morphine/codeine class opioid has an equivalent nitrogen derivative such as hydromorphone-N-oxide.
References
- ↑ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ↑ Phillipson, J. David; El-Dabbas, Samia W.; Gorrod, John W. (1978). "In vivo and in vitro N-oxidation of morphine and codeine". Biol. Oxid. Nitrogen, Proc. Int. Symp., 2nd: 125–30.
- ↑ 21 CFR 1308.11
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.