Levophenacylmorphan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Levophenacylmorphan |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.168 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
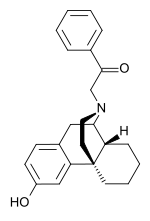
| Formula | C24H27NO2 |
| Molar mass | 361.485 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Levophenacylmorphan is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It has potent analgesic effects and is around 10x more potent than morphine.[2] Adverse effects associated with its use are those of the opioids as a whole, including pruritus, nausea, respiratory depression, euphoria and development of tolerance and dependence to its effects.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ↑ May E, Eddy N (February 1959). "A New Potent Synthetic Analgesic". Communications. The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 24 (2): 294–5. doi:10.1021/jo01084a655.
- ↑ Fraser HF, Isbell H (January 1960). "Human pharmacology and addiction liabilities of phenazocine and levophenacylmorphan". Bulletin on Narcotics. 12 (2): 15–23.
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.