| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
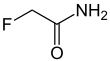
| IUPAC name
2-Fluoroacetamide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.331 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4FNO | |||
| Molar mass | 77.058 | ||
| Melting point | 107 to 109 °C (225 to 228 °F; 380 to 382 K) | ||
| Soluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Fluoroacetamide is an organic compound based on acetamide with one fluorine atom replacing hydrogen on the methyl group. it is a metabolic poison which disrupts the citric acid cycle and was used as a rodenticide.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ MATSUMURA F, O'BRIEN RD. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE MODES OF ACTION OF FLUOROACETAMIDE AND FLUOROACETATE IN THE MOUSE AND AMERICAN COCKROACH. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Oct;12:1201-5.doi:10.1016/0006-2952(63)90095-9 PMID 14074120
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.