Clidinium bromide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601036 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Low |
| Excretion | Kidney and biliary |
| Chemical and physical data | |
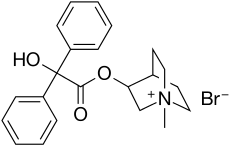
| Formula | C22H26NO3+ |
| Molar mass | 352.454 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Clidinium bromide is an anticholinergic (specifically a muscarinic antagonist) medication.[1] It may help symptoms of cramping and abdominal pain by slowing the intestines.
In the United States it is only commercially available in combination with chlordiazepoxide (a benzodiazepine) as chlordiazepoxide/clidinium.[2]
Mechanism of action
Clidinium inhibits muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on smooth muscles, secretory glands, and in the central nervous system to relax smooth muscle and decrease biliary tract secretions.[3]
References
- ↑ "Clidinium bromide". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on August 28, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2013.
- ↑ "Clidinium Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 28 August 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ↑ 2014 Nurses Drug Handbook (13th ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning. 2014. pp. 245-6. ISBN 978-1-284-03115-7.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.