Ebalzotan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
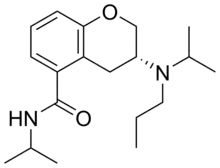
| Formula | C19H30N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 318.461 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Ebalzotan (NAE-086) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist.[1][2] It was under development as an antidepressant and anxiolytic agent but produced undesirable side effects in phase I clinical trials and was subsequently discontinued.[1][2]
See also
References
- 1 2 Braish T, Gadamasetti KG (2008). Process chemistry in the pharmaceutical industry, volume 2 challenges in an ever changing climate. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-9051-7.
- 1 2 Weaver DF, Nogrady T, Nogrady T (2005). Medicinal chemistry a molecular and biochemical approach. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-510455-2.
| 5-HT1ARTooltip 5-HT1A receptor agonists | |
|---|---|
| GABAARTooltip GABAA receptor PAMsTooltip positive allosteric modulators |
|
| Hypnotics | |
| Gabapentinoids (α2δ VDCC blockers) | |
| Antidepressants |
|
| Antipsychotics | |
| Sympatholytics (Antiadrenergics) |
|
| Others | |
| |
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.