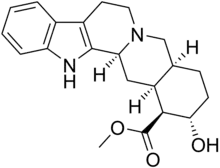
Rauwolscine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.553 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 354.450 g·mol−1 |
InChI
| |
| | |
Rauwolscine, also known as isoyohimbine, α-yohimbine, and corynanthidine, is an alkaloid found in various species within the genera Rauvolfia and Corynanthe (including Pausinystalia).[1] It is a stereoisomer of yohimbine.[1] Rauwolscine is a central nervous system stimulant, a local anesthetic and a vague aphrodisiac.[1]
Rauwolscine acts predominantly as a α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist.[2][3] It has also been shown to function as a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist and 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptor antagonist.[4][5][6]
See also
- Ajmalicine
- Corynanthine
- Spegatrine
- Yohimbine
References
- 1 2 3 Kohli JD, De NN (June 1956). "Pharmacological action of rauwolscine". Nature. 177 (4521): 1182. Bibcode:1956Natur.177.1182K. doi:10.1038/1771182a0. PMID 13334509. S2CID 4212268.
- ↑ Perry BD, U'Prichard DC (December 1981). "[3H]rauwolscine (alpha-yohimbine): a specific antagonist radioligand for brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptors". European Journal of Pharmacology. 76 (4): 461–464. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(81)90123-0. PMID 6276200.
- ↑ Qin K, Sethi PR, Lambert NA (August 2008). "Abundance and stability of complexes containing inactive G protein-coupled receptors and G proteins". FASEB Journal. 22 (8): 2920–2927. doi:10.1096/fj.08-105775. PMC 2493464. PMID 18434433.
- ↑ Arthur JM, Casañas SJ, Raymond JR (June 1993). "Partial agonist properties of rauwolscine and yohimbine for the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by recombinant human 5-HT1A receptors". Biochemical Pharmacology. 45 (11): 2337–2341. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(93)90208-E. PMID 8517875.
- ↑ Kaumann AJ (June 1983). "Yohimbine and rauwolscine inhibit 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced contraction of large coronary arteries of calf through blockade of 5 HT2 receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 323 (2): 149–154. doi:10.1007/BF00634263. PMID 6136920. S2CID 23251900.
- ↑ Wainscott DB, Sasso DA, Kursar JD, Baez M, Lucaites VL, Nelson DL (January 1998). "[3H]Rauwolscine: an antagonist radioligand for the cloned human 5-hydroxytryptamine2b (5-HT2B) receptor". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 357 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1007/PL00005133. PMID 9459568. S2CID 28910390. Archived from the original on 2001-09-11.
| Dopamine agonists | |
|---|---|
| Melanocortin agonists | |
| PDE5 inhibitors | |
| Sex steroids |
|
| Others |
|
| |
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.