QL (chemical)
.svg.png.webp) | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-[Di(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl ethyl methylphosphonite | |
| Other names
2-(Diisopropylamino)ethyl ethyl methylphosphonite N-[2-(Ethoxy(methyl)phosphanyl)oxyethyl]-N-isopropyl-propan-2-amine Isopropyl aminoethylmethyl phosphonite O-(2-Diisopropylaminoethyl) O'-ethyl methylphosphonite | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | QL |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
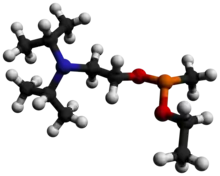
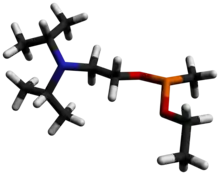
Chemical formula |
C11H26NO2P |
| Molar mass | 235.308 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Strong fishy odor |
| Boiling point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K) |
Solubility in water |
Slightly soluble in water |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Isopropyl aminoethylmethyl phosphonite (NATO designation QL), also known as O-(2-diisopropylaminoethyl) O′-ethyl methylphosphonite, is a precursor chemical to the nerve agent VX and VR-56. It is a colorless liquid with a strong fishy odor, and is slightly soluble in water.[1]
Synthesis
QL is manufactured by reacting diethyl methylphosphonite with 2-(diisopropylamino)ethanol.[2]
Uses in chemical warfare
QL is a component in binary chemical weapons, mainly VX nerve agent.[3] It, along with methylphosphonyl difluoride (DF), was developed during the 1980s in order to replace an aging stockpile of unitary chemical weapons.[3] QL is listed as a Schedule 1 chemical by the Chemical Weapons Convention.[4]
Toxicity
QL itself is a relatively non-toxic chemical.[5] However, when reacting with sulfur, the corresponding sulfide of QL isomerizes into the highly toxic VX molecule.[3][5]
References
- ↑ "Isopropyl aminoethylmethyl phosphonite". PubChem.
- ↑ "Isopropyl aminoethylmethyl phosphonite". PubChem.
- 1 2 3 National Research Council, et al. Systems and Technologies for the Treatment of Non-stockpile Chemical Warfare Materiel, (Google Books), National Academies Press, 2002, p. 14, (ISBN 0309084520), accessed October 21, 2008.
- ↑ "Schedule One Chemicals", Chemical Weapons Convention Archived 2012-01-03 at the Wayback Machine, US Government website, Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- 1 2 Croddy, Eric and Wirtz, James J. Weapons of Mass Destruction: An Encyclopedia of Worldwide Policy, Technology, and History, (Google Books), ABC-CLIO, 2005, p. 238, (ISBN 1851094903), accessed October 21, 2008.