BML-190
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
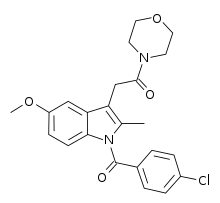
| Formula | C23H23ClN2O4 |
| Molar mass | 426.90 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
BML-190 (Indomethacin morpholinylamide) is a drug used in scientific research that acts as a selective CB2 inverse agonist.[1] BML-190 is structurally derived from the NSAID indomethacin but has a quite different biological activity.[2] The activity produced by this compound is disputed, with some sources referring to it as a CB2 agonist rather than an inverse agonist;[3][4] this may reflect an error in classification, or alternatively it may produce different effects in different tissues, and more research is required to resolve this dispute.
References
- ↑ New DC, Wong YH (February 2003). "BML-190 and AM251 act as inverse agonists at the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor: signalling via cAMP and inositol phosphates". FEBS Letters. 536 (1–3): 157–60. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00048-6. PMID 12586356. S2CID 38569901.
- ↑ Klegeris A, Bissonnette CJ, McGeer PL (June 2003). "Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor". British Journal of Pharmacology. 139 (4): 775–86. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705304. PMC 1573900. PMID 12813001.
- ↑ Melck D, De Petrocellis L, Orlando P, Bisogno T, Laezza C, Bifulco M, Di Marzo V (January 2000). "Suppression of nerve growth factor Trk receptors and prolactin receptors by endocannabinoids leads to inhibition of human breast and prostate cancer cell proliferation". Endocrinology. 141 (1): 118–26. doi:10.1210/endo.141.1.7239. PMID 10614630.
- ↑ Scutt A, Williamson EM (January 2007). "Cannabinoids stimulate fibroblastic colony formation by bone marrow cells indirectly via CB2 receptors". Calcified Tissue International. 80 (1): 50–9. doi:10.1007/s00223-006-0171-7. PMID 17205329. S2CID 23624771.
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.