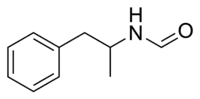
Formetorex
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(1-Phenylpropan-2-yl)formamide | |
| Other names
Formetorex N-Formylamphetamine N-(alpha-Methylphenethyl)formamide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference |
1563 |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C10H13NO |
| Molar mass | 163.220 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Formetorex (INN), also known as formetamide or N-formylamphetamine, is a substituted amphetamine described as an anorectic which does not appear to have ever been marketed.[1]
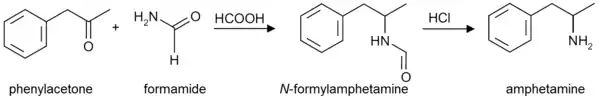
Formetorex is also an intermediate in the production of amphetamine by the "Leuckart reaction."[2] It is also commonly found as an impurity in clandestine labs where this synthesis method is used.[2][3] Due to the simplicity of the Leuckart reaction, it is the most popular synthetic route employed for the illicit manufacture of amphetamines.[2] The synthesis involves a non-metal reduction that is typically carried out in three steps.[2] For amphetamine synthesis, a mixture of phenylacetone and formamide (sometimes in the presence of formic acid) or ammonium formate, is heated until a condensation reaction results in the intermediate product, formetamide.[2] In the second step, formetamide is hydrolysed using hydrochloric acid, and the reaction mixture is then basified, isolated, and steam distilled to produce the free base.[2] The final step, the product is dissolved in an organic solvent and precipitated as the sulphate salt of amphetamine by adding sulfuric acid.[2]
Amphetamine synthesis via the Leuckart reaction
|
References
- ↑ Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 568–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Laboratory and Scientific Section (2006). Recommended methods of the identification and analysis of amphetamine, methamphetamine, and their ring-substituted analogues in seized materials (PDF). New York: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime Vienna. ISBN 92-1-148208-9. Retrieved 14 October 2013.
- ↑ Kram TC (July 1979). "Reidentification of a major impurity in illicit amphetamine". Journal of Forensic Sciences. 24 (3): 596–9. doi:10.1520/JFS10875J. PMID 541629.
External links
- formetamide at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)