Butidrine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
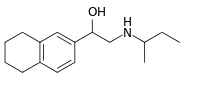
| IUPAC name
2-(Butan-2-ylamino)-1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)ethanol | |
| Other names
Butedrine; Butydrine; Hydrobutamine; Idrobutamine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C16H25NO |
| Molar mass | 247.382 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Butidrine (INN) (brand names Betabloc, Butidrate, Recetan), or butedrine or butydrine, also known as hydrobutamine or idrobutamine, is a beta blocker related to pronethalol[1] and propranolol[2] that was developed in the 1960s.[3][4] Similarly to certain other beta blockers, butidrine also possesses local anesthetic properties.[5]
References
- ↑ Bristol JA (1986). Cardiovascular drugs. John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated. p. 111. ISBN 978-0-471-09228-5.
- ↑ Drug Metabolism Reviews. Marcel Dekker. 1972.
- ↑ Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 58–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 197–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Charlier R (1971). Antianginal drugs: pathophysiological, haemodynamic, methodological, pharmacological, biochemical and clinical basis for their use in human therapeutics. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-3-540-05365-1.
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.