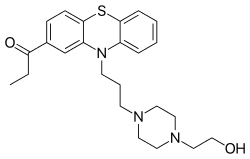
Carfenazine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Proketazine, Carphenazin |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.249 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H31N3O2S |
| Molar mass | 425.59 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Carfenazine (INN) (former developmental code name WY-2445), or carphenazine (BAN), also known as carphenazine maleate (USAN) (brand name Proketazine; former developmental code name NSC-71755), is an antipsychotic and tranquilizer of the phenothiazine group that was withdrawn from the market.[1][2][3]
Synthesis
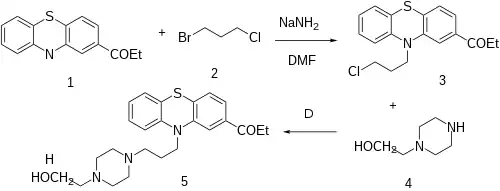
The alkylation reaction between 2-Propionyl Phenothiazine [92-33-1] (1) and 1-Bromo-3-chloropropane (2) gives 1-[10-(3-chloropropyl)phenothiazin-2-yl]propan-1-one [95157-45-2] (3). A second alkylation step, this time with 2-(1-Piperazinyl)ethanol [103-76-4] (4) completes the synthesis of Carfenazine (5).
NB: Although above procedure is proof-of-concept, bear in mind no protecting group {Other patent uses ketalization technique}
Analogues
- Butaperazine uses butanoyl (Butyryl) and not propanoyl group.
- Fluphenazine selfsame but trifluoromethyl on position 2 of the phenothiazine ring.
References
- ↑ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 224–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 862–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- ↑ Briggs GG, Freeman RK, Yaffe SJ (2011). Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation: A Reference Guide to Fetal and Neonatal Risk. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 213–. ISBN 978-1-60831-708-0.
- ↑ Zhuraulev, S.V. et al, Zh. Obshch. Khim., 1962, 32, 2244
- ↑ M. H. Sherlock, N. Sperber, U.S. patent 2,985,654 (1961 to Schering)
- ↑ R. F. Tislow et al., U.S. patent 3,023,146 (1962 to American Home Products).
| Typical |
|
|---|---|
| Disputed | |
| Atypical |
|
| Others |
|
| |
Acetylcholine receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D1-like |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||||
| |||||||
Histamine receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 |
| ||||
| H2 |
| ||||
| H3 |
| ||||
| H4 |
| ||||
| |||||
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Anticholinergics | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.