Pinoxepin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pinoxepine; P-5227 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
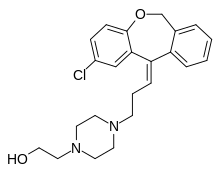
| Formula | C23H27ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 398.93 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Pinoxepin (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name; developmental code name P-5227; pinoxepin hydrochloride (USANTooltip United States Adopted Name)) is an antipsychotic of the tricyclic group with a dibenzoxepin ring system which was developed in the 1960s but was never marketed.[1][2][3][4][5] It was found in clinical trials to have effectiveness in the treatment of schizophrenia similar to that of chlorpromazine and thioridazine.[4] The drug has marked sedative effects but causes relatively mild extrapyramidal symptoms.[2][4]
References
- ↑ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 984–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- 1 2 Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. 1 January 1967. pp. 2–. ISBN 978-0-08-058346-4.
- ↑ Gordon M (2 December 2012). Psychopharmacological Agents. Elsevier Science. pp. 102–. ISBN 978-0-323-15128-3.
- 1 2 3 Iversen L (6 December 2012). Handbook of Psychopharmacology: Volume 10: Neoroleptics and Schizophrenia. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 200–. ISBN 978-1-4613-4042-3.
- ↑ Lajtha A (11 November 2013). Alterations of Metabolites in the Nervous System. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 335–. ISBN 978-1-4757-6740-7.
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Anticholinergics | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wmcloud. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.